Lisbon is one of the oldest cities in the world and the second-oldest European capital city (after Athens), predating other modern European capitals by centuries. Settled by pre-Celtic tribes and later founded and civilized by the Phoenicians, Julius Caesar made it a municipium called Felicitas Julia, adding the term to the name Olissipo. After the fall of the Roman Empire, it was ruled by a series of Germanic tribes from the 5th century, most notably the Visigoths. Later it was captured by the Moors in the 8th century. In 1147 Afonso Henriques conquered the city and in 1255 it became Portugal's capital, replacing Coimbra.








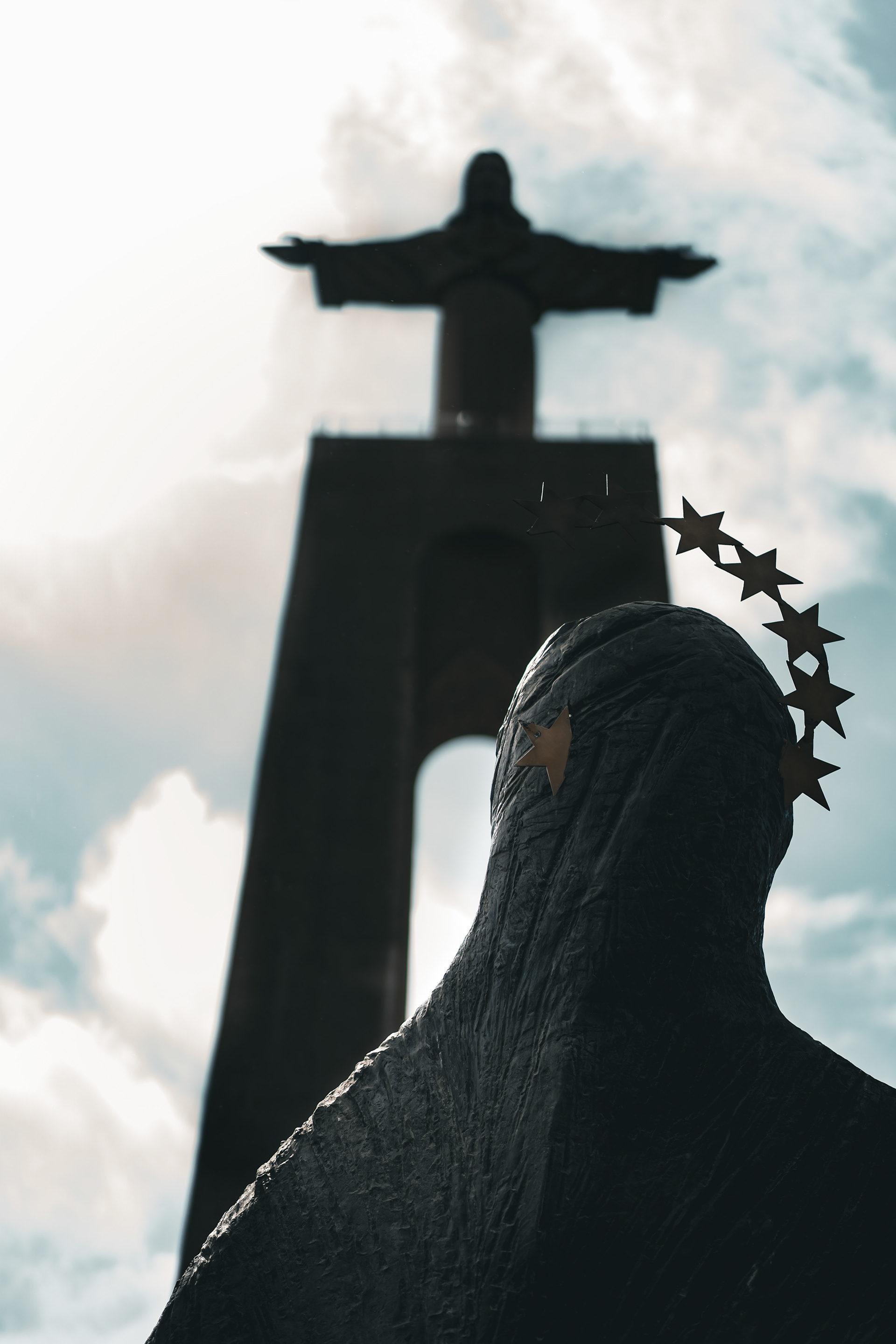
The construction of the Christ the King monument was approved in a Portuguese Episcopate conference, held in Fatima on 20 April 1940, as a plea to God to release Portugal from entering World War II and celebrate the 50th anniversary of the act of consecration of the world to the Sacred Heart of Jesus. However, the idea had originated earlier on a visit of the Cardinal Patriarch of Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro in 1934, soon after the inauguration of the statue of Christ the Redeemer in 1931.
The 25 de Abril Bridge is based in part on two San Francisco Bay Area bridges. Its paint is the same International Orange color as the famous Golden Gate Bridge, and the design is similar as well to the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge. Both the Bay Bridge and the 25 de Abril Bridge were built by the same company.








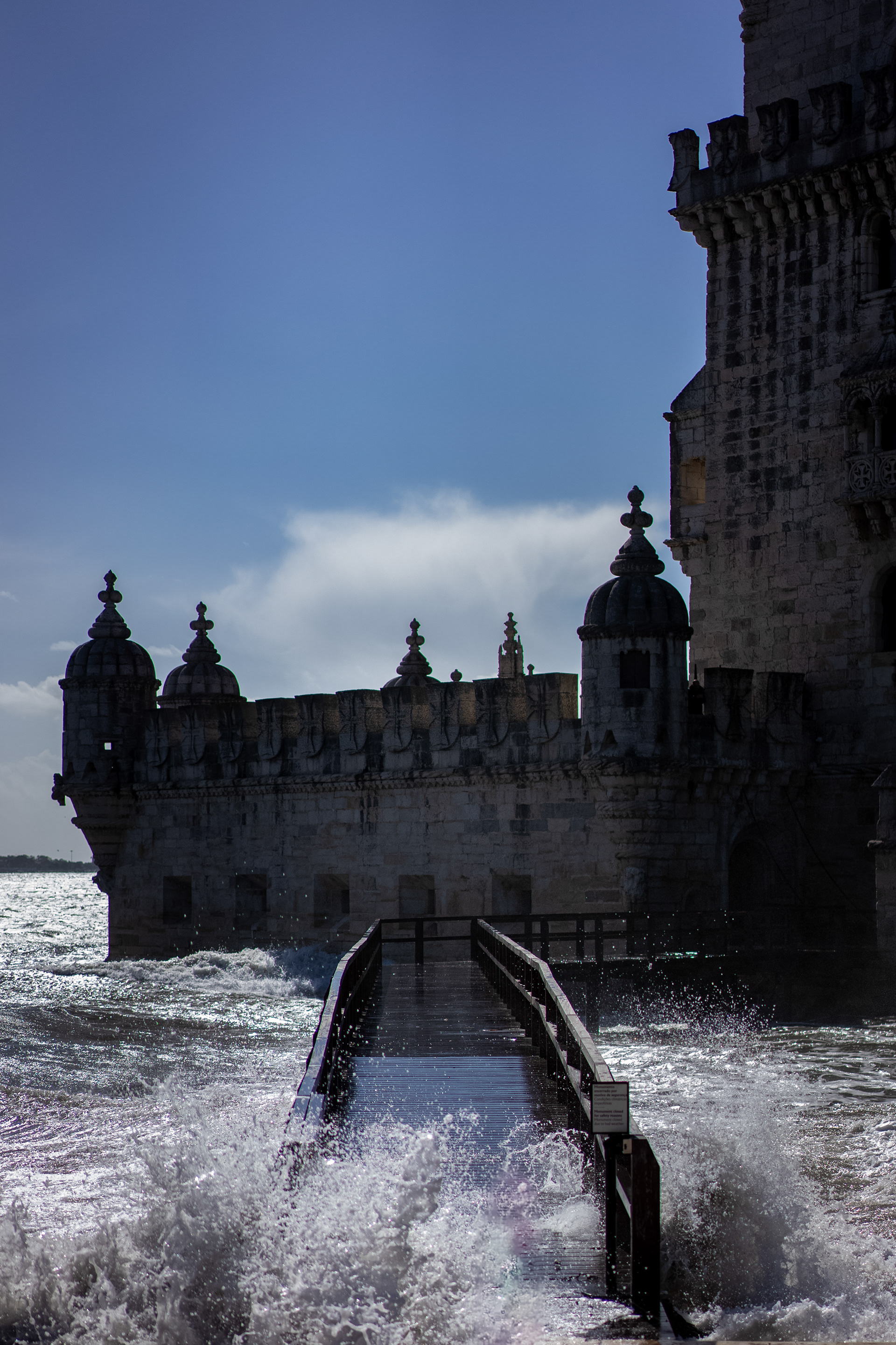
Belém Tower, officially the Tower of Saint Vincent is a 16th-century fortification located in Lisbon that served as a point of embarkation and disembarkation for Portuguese explorers and as a ceremonial gateway to Lisbon. This tower symbolizes Portugal's maritime and colonial power in early modern Europe.
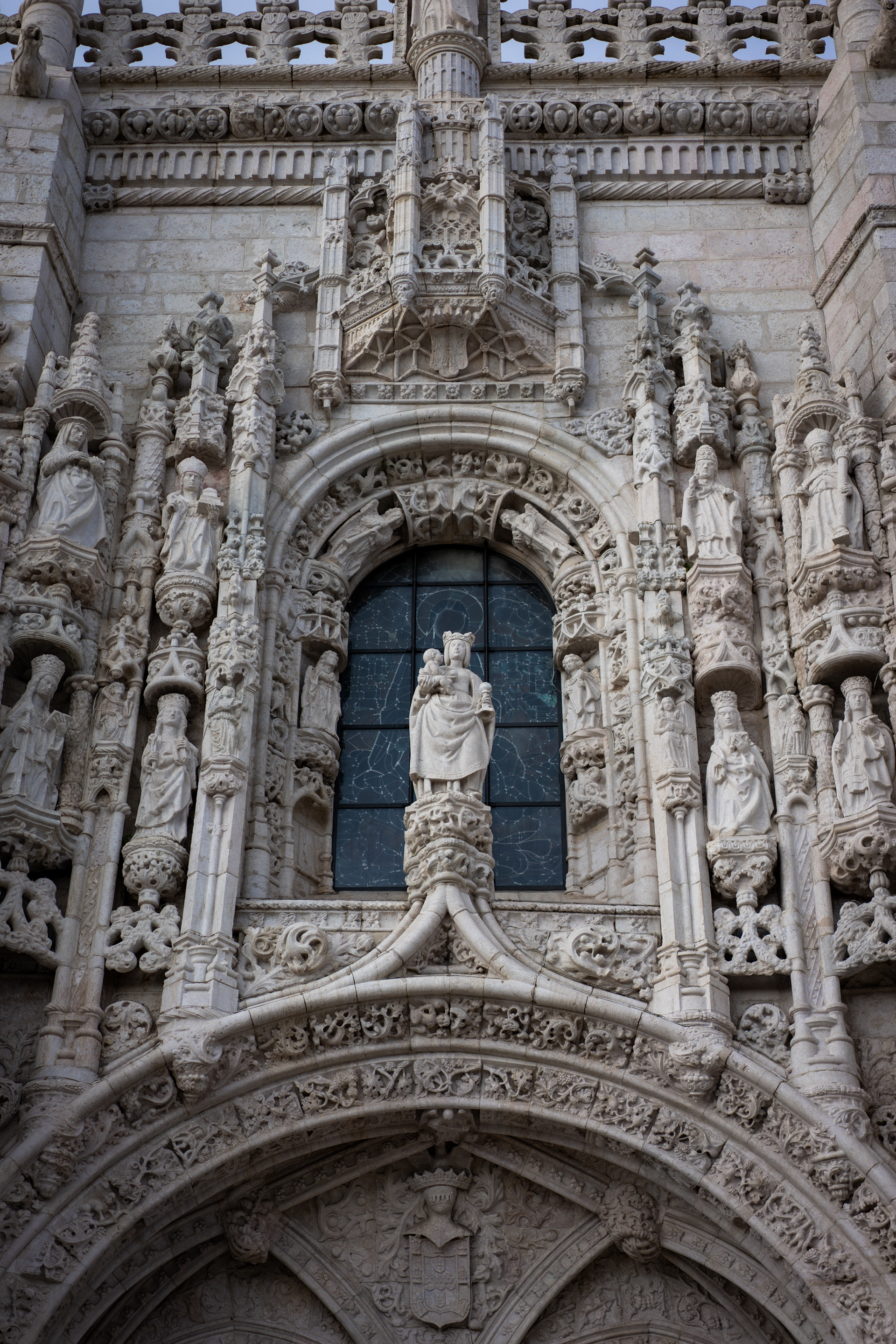
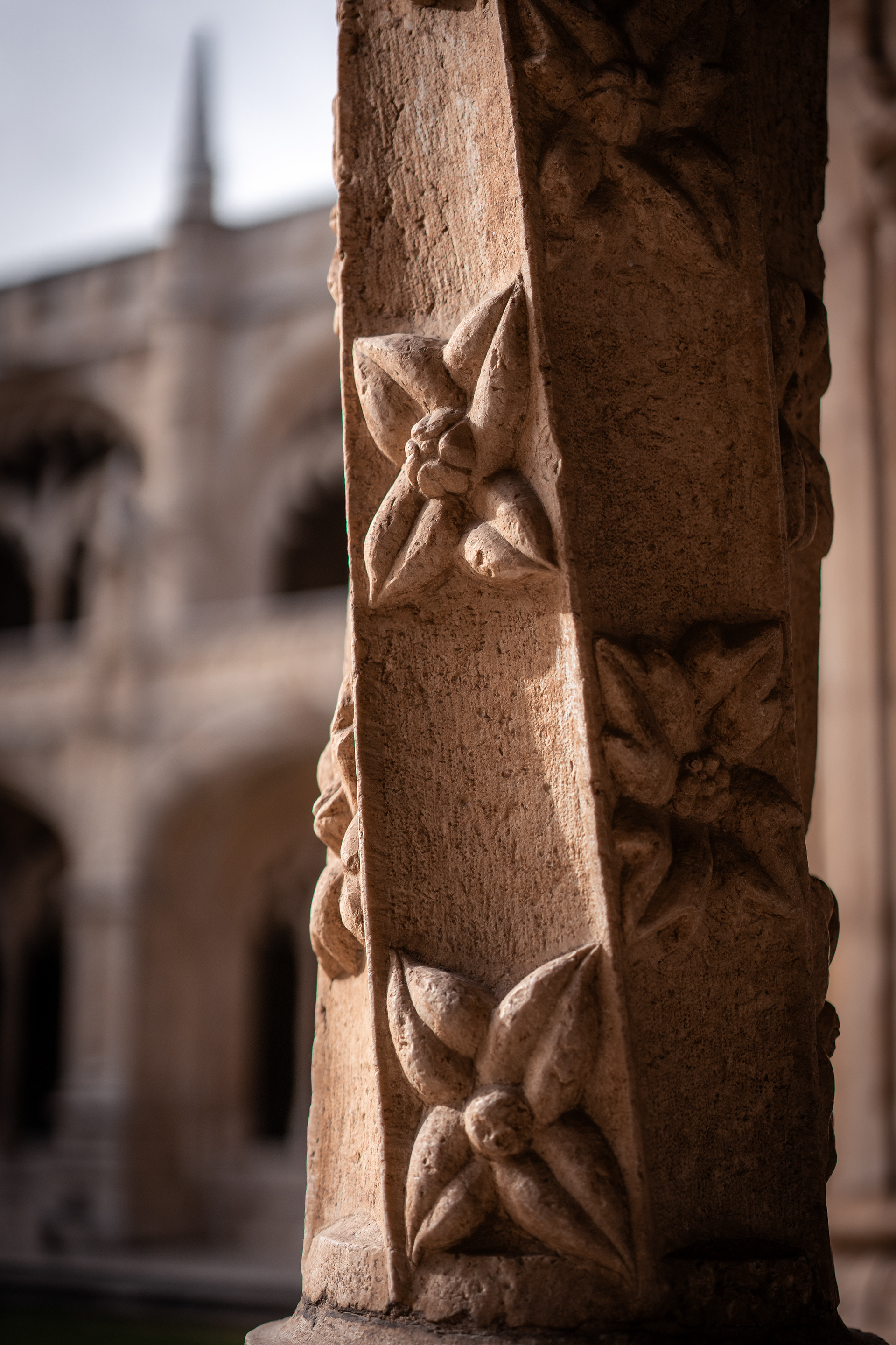
Discoveries by Portuguese navigators transformed Lisbon into the world’s main trade hub in the 15th and 16th centuries. To protect the city, King João II conceived a pioneer project to defend Lisbon from enemy ships, a work completed in 1514 and which included the building of the Belém Tower, designed by architect Francisco de Arruda. The tower’s unique design includes a modern and heavily armed bastion, protruding over the river.


The construction of the monastery and church began on 6 January 1501, and was completed 100 years later. King Manuel originally funded the project with money obtained from the Vintena da Pimenta, a 5 percent tax on commerce from Africa and the Orient, equivalent to 70 kilograms of gold per year, with the exception of those taxes collected on the importation of pepper, cinnamon and cloves, which went directly to the Crown.
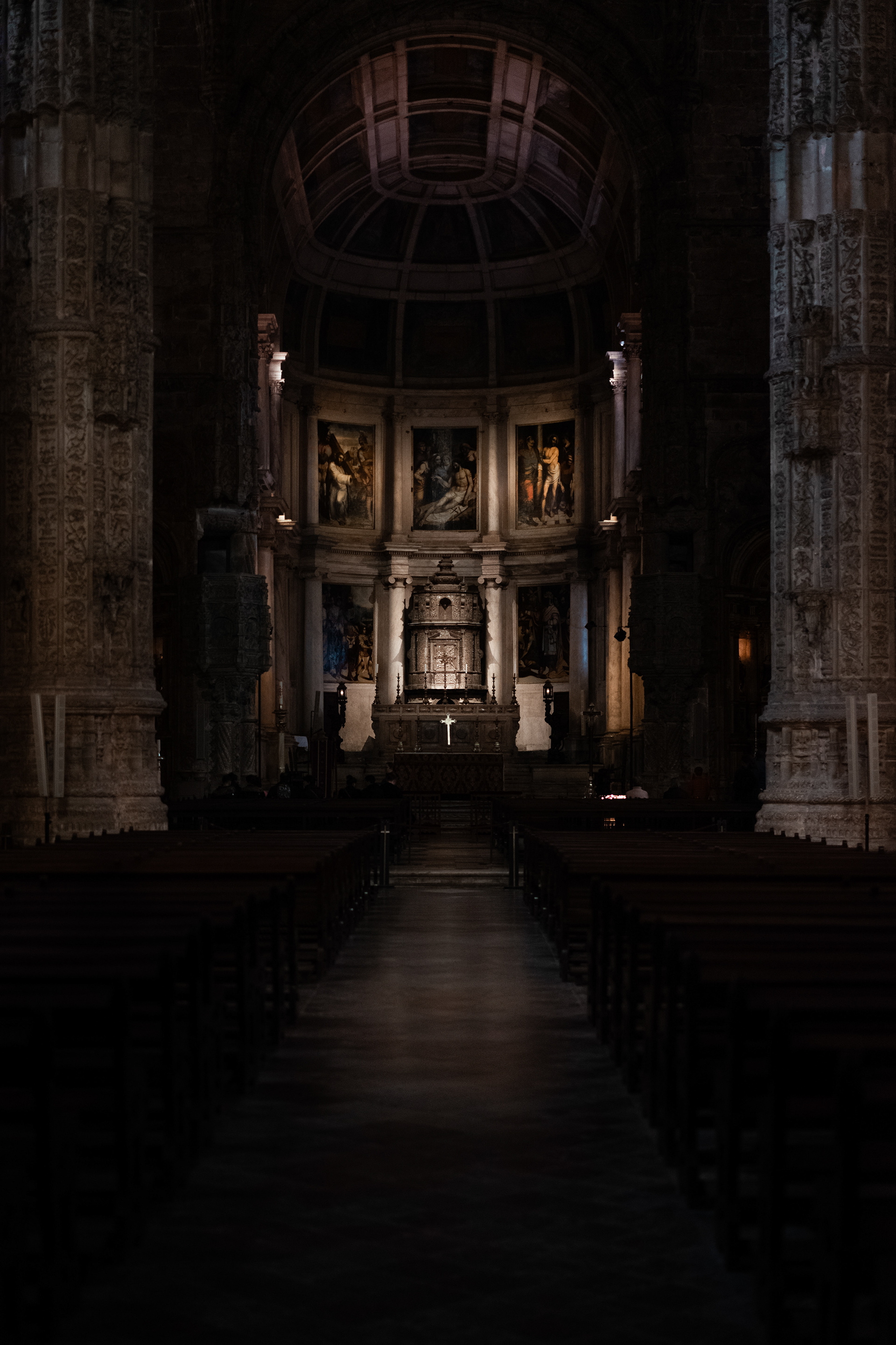
The Monastery of the Hieronymites, in Belém, which would become the necropolis of the Portuguese royal dynasty of Aviz, was erected in the early 1500s near the launch point of Vasco da Gama's first journey, and its construction funded by a tax on the profits of the yearly Portuguese India Armadas. In 1880, da Gama's remains and those of the poet Luís de Camões were moved to new carved tombs in the nave of the monastery's church, only a few meters away from the tombs of the kings Manuel I and John III, whom da Gama had served.












The Pombaline Baixa is an elegant district, primarily constructed after the 1755 Lisbon earthquake. It takes its name from Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, 1st Marquis of Pombal, the prime minister to Joseph I of Portugal from 1750 to 1777 and key figure of the Enlightenment in Portugal, who took the lead in ordering the rebuilding of Lisbon after the 1755 earthquake. The Marquis of Pombal imposed strict conditions on rebuilding the city, and the current grid pattern strongly differs from the organic streetplan that characterised the district before the earthquake.
The Pombaline Baixa is one of the first examples of earthquake-resistant construction. Architectural models were tested by having troops march around them to simulate an earthquake. Notable features of Pombaline structures include the Pombaline cage, a symmetrical wood-lattice framework aimed at distributing earthquake force, and inter-terrace walls that are built higher than roof timbers to reduce fire contagion.




The area includes the Sintra-Cascais Nature Park through which the Sintra Mountains run. The historic center of the Vila de Sintra is famous for its 19th-century Romanticist architecture, historic estates and villas, gardens, and royal palaces and castles, which resulted in the classification of the town as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Sintra's landmarks include the medieval Castle of the Moors, the romanticist Pena National Palace and the Portuguese Renaissance Sintra National Palace.
Traces of several Bronze Age remains were also discovered in many places in the Sintra Mountains, including alongside the town, in the Monte do Sereno area, and a late Bronze Age settlement within the Moorish Castle dating to the 9th–6th centuries B.C. The most famous object from this period is the so-called Sintra Collar, a middle Bronze Age gold neck-ring found near the city at the end of the 19th century, which since 1900 has been part of the British Museum's collection.












In 1493, King John II, accompanied by his wife Queen Leonor, made a pilgrimage to the site to fulfil a vow. His successor, King Manuel I, was also very fond of this sanctuary, and ordered the construction of a monastery on this site which was donated to the Order of Saint Jerome. For centuries Pena was a small, quiet place for meditation, housing a maximum of eighteen monks.
The castle's history started in the Middle Ages when a chapel dedicated to Our Lady of Pena was built on the top of the hill above Sintra. According to tradition, construction occurred after an apparition of the Virgin Mary. Side view of the palace. The palace seen from above In 1493, King John II, accompanied by his wife Queen Leonor, made a pilgrimage to the site to fulfil a vow. His successor, King Manuel I, was also very fond of this sanctuary, and ordered the construction of a monastery on this site which was donated to the Order of Saint Jerome. For centuries Pena was a small, quiet place for meditation, housing a maximum of eighteen monks