Paris was founded in the 3rd century B.C. on Île de la Cité by a community of Celts. They were a group of tribal fishermen called the Parisii who, pushed by emigration towards the banks of the Seine, made a permanent settlement there and profited from the area’s fertility and temperate climate.
At the time of the Parisii’s settlement in the area, there were seven islands on the river between what is now the pont d'Austerlitz and the pont des Arts. . In giving them their modern names, the first was the Ile Louviers (which existed until 1843, when it was reunited with the mainland to become Quai Henri IV), Ile Saint-Louis was divided into three islets which were successively joined to each other, the same was the case for Ile de la Cité, which was originally three separate islets.
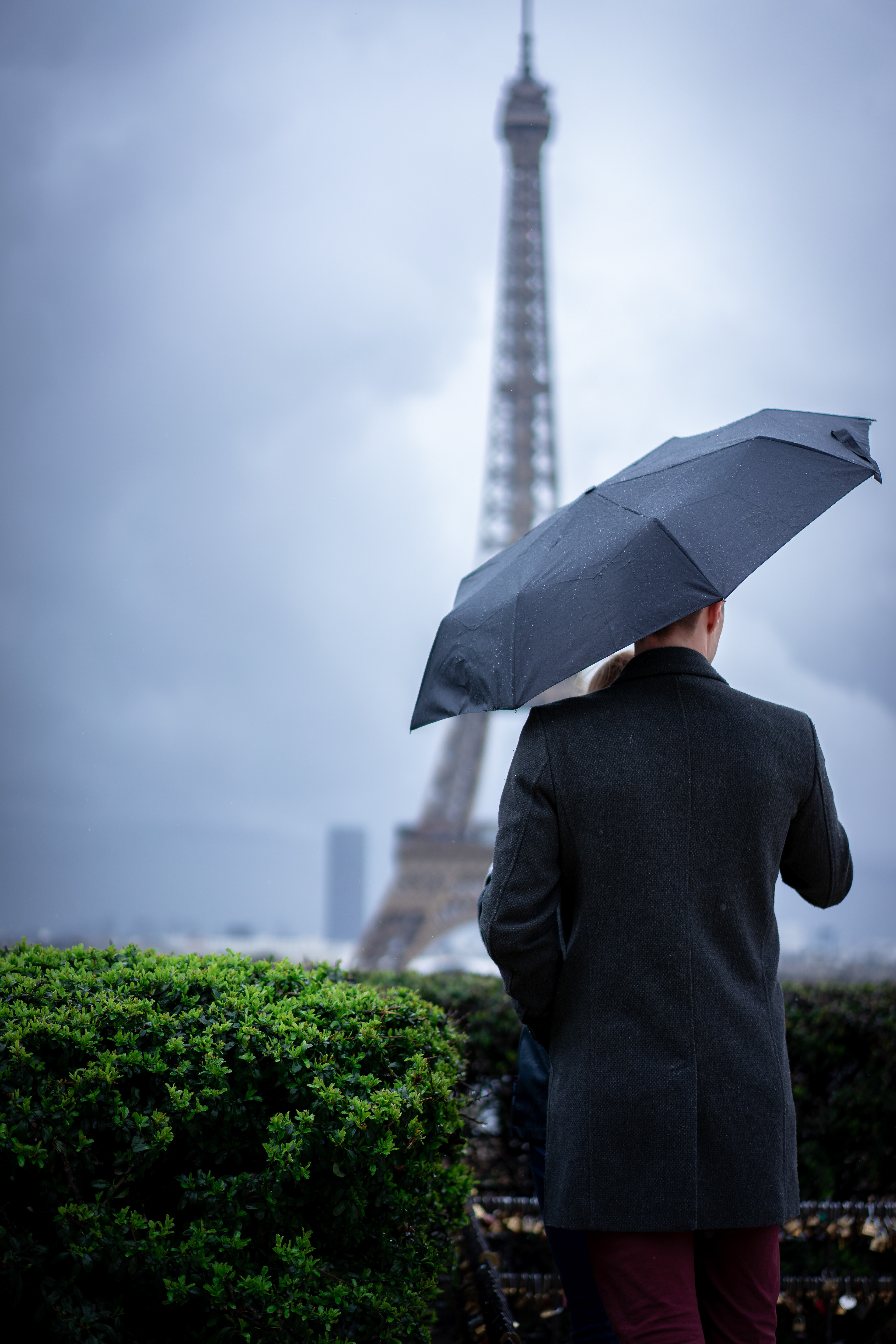
Locally nicknamed "La dame de fer" (French for "Iron Lady"), Eiffel Tower was constructed as the centrepiece of the 1889 World's Fair, and to crown the centennial anniversary of the French Revolution. Although initially criticised by some of France's leading artists and intellectuals for its design, it has since become a global cultural icon of France and one of the most recognisable structures in the world.
Gustave Eiffel engraved on the tower the names of 72 French scientists, engineers and mathematicians in recognition of their contributions to the building of the tower. Eiffel chose this "invocation of science" because of his concern over the artists' protest. At the beginning of the 20th century, the engravings were painted over, but they were restored in 1986–87 by the Société Nouvelle d'exploitation de la Tour Eiffel, a company operating the tower.


















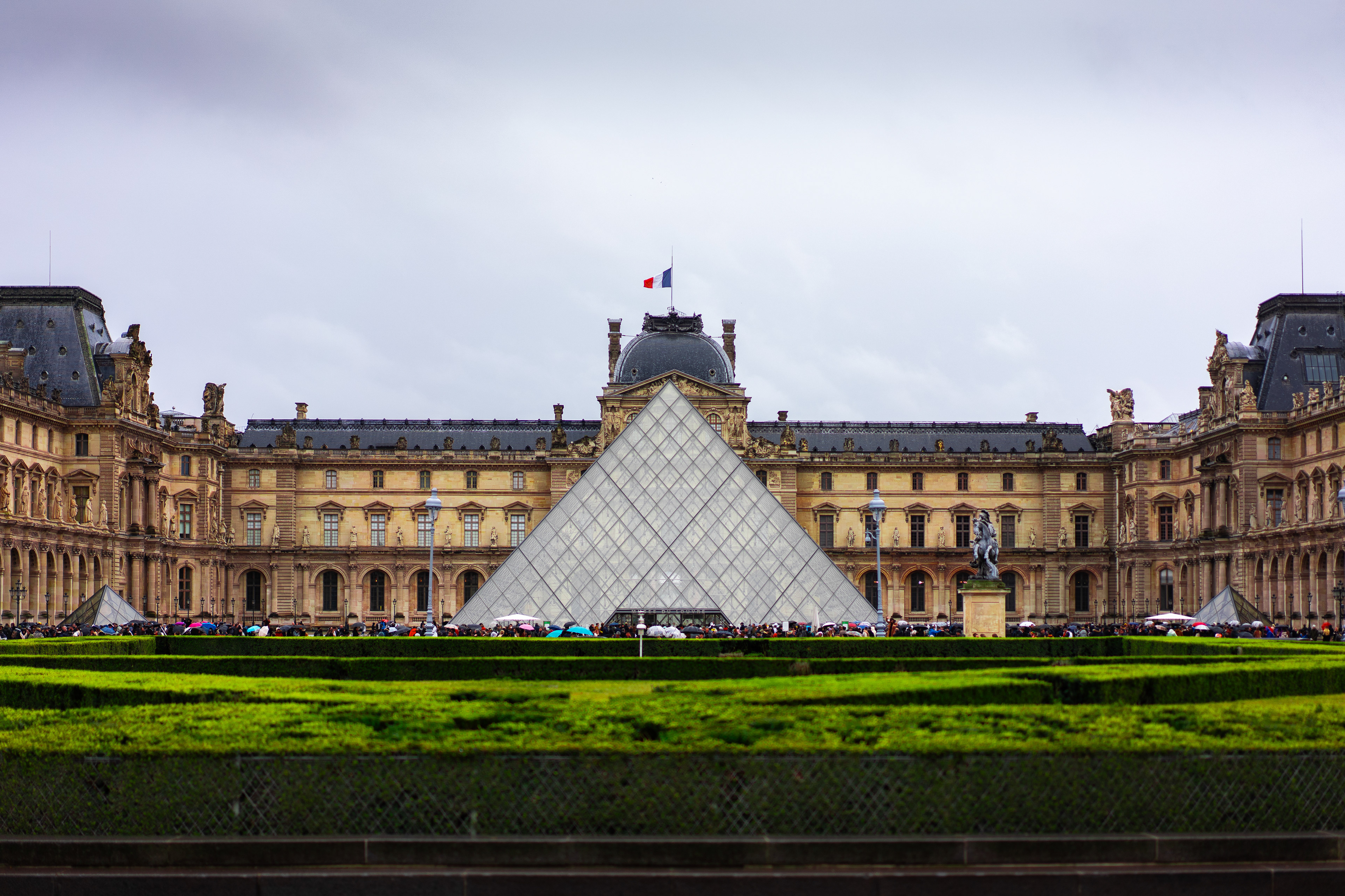
The Louvre museum is housed in the Louvre Palace, originally built in the late 12th to 13th century under Philip II. Remnants of the Medieval Louvre fortress are visible in the basement of the museum. Due to urban expansion, the fortress eventually lost its defensive function, and in 1546 Francis I converted it into the primary residence of the French kings. The building was extended many times to form the present Louvre Palace. In 1682, Louis XIV chose the Palace of Versailles for his household, leaving the Louvre primarily as a place to display the royal collection, including, from 1692, a collection of ancient Greek and Roman sculpture.
The origins of the name "Louvre" are somewhat disputed. According to the authoritative Grand Larousse encyclopédique, the name derives from an association with a wolf hunting den. In the 7th century, Burgundofara (also known as Saint Fare), abbess in Meaux, is said to have gifted part of her "Villa called Luvra situated in the region of Paris" to a monastery, even though it is doubtful that this land corresponded exactly to the present site of the Louvre.
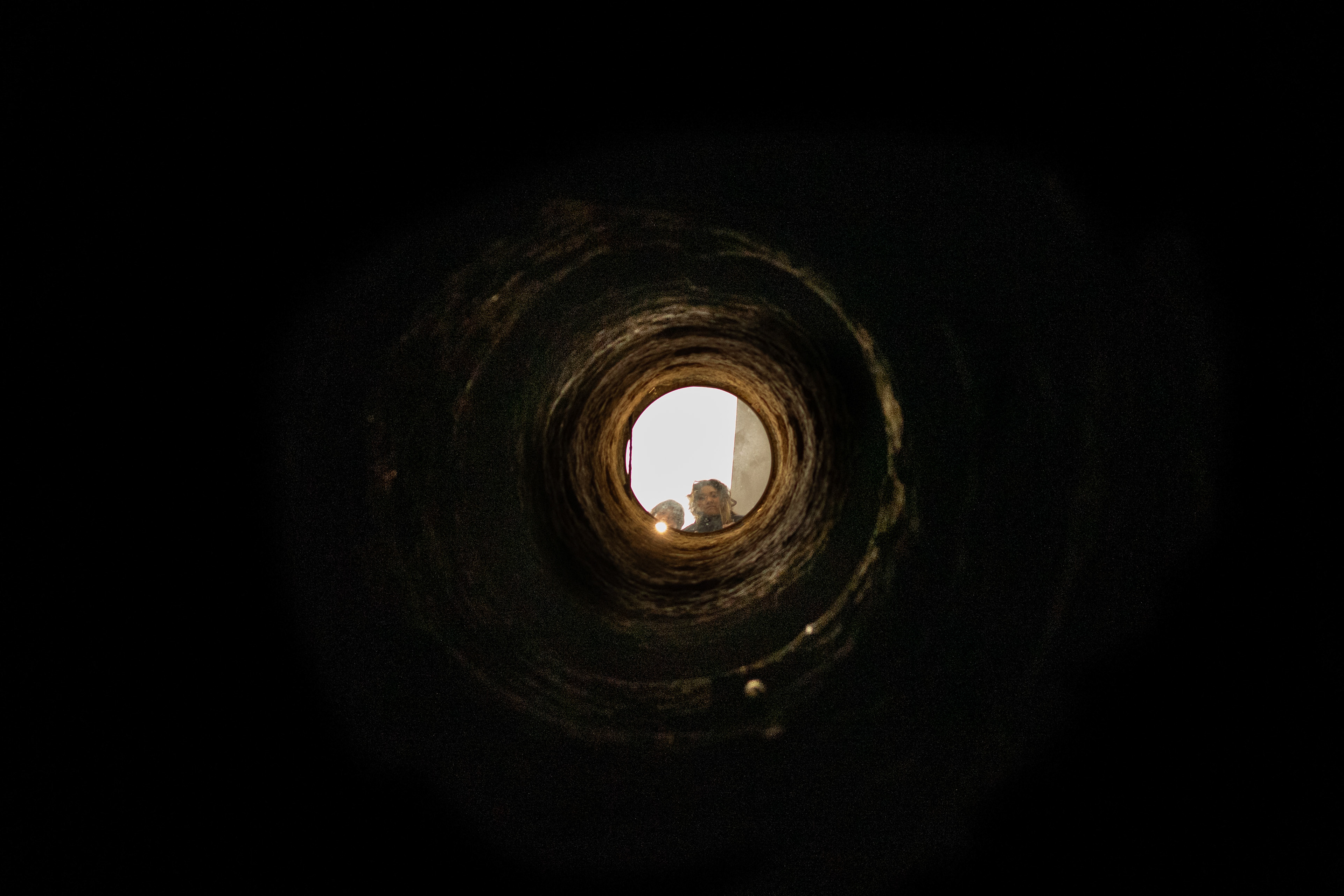
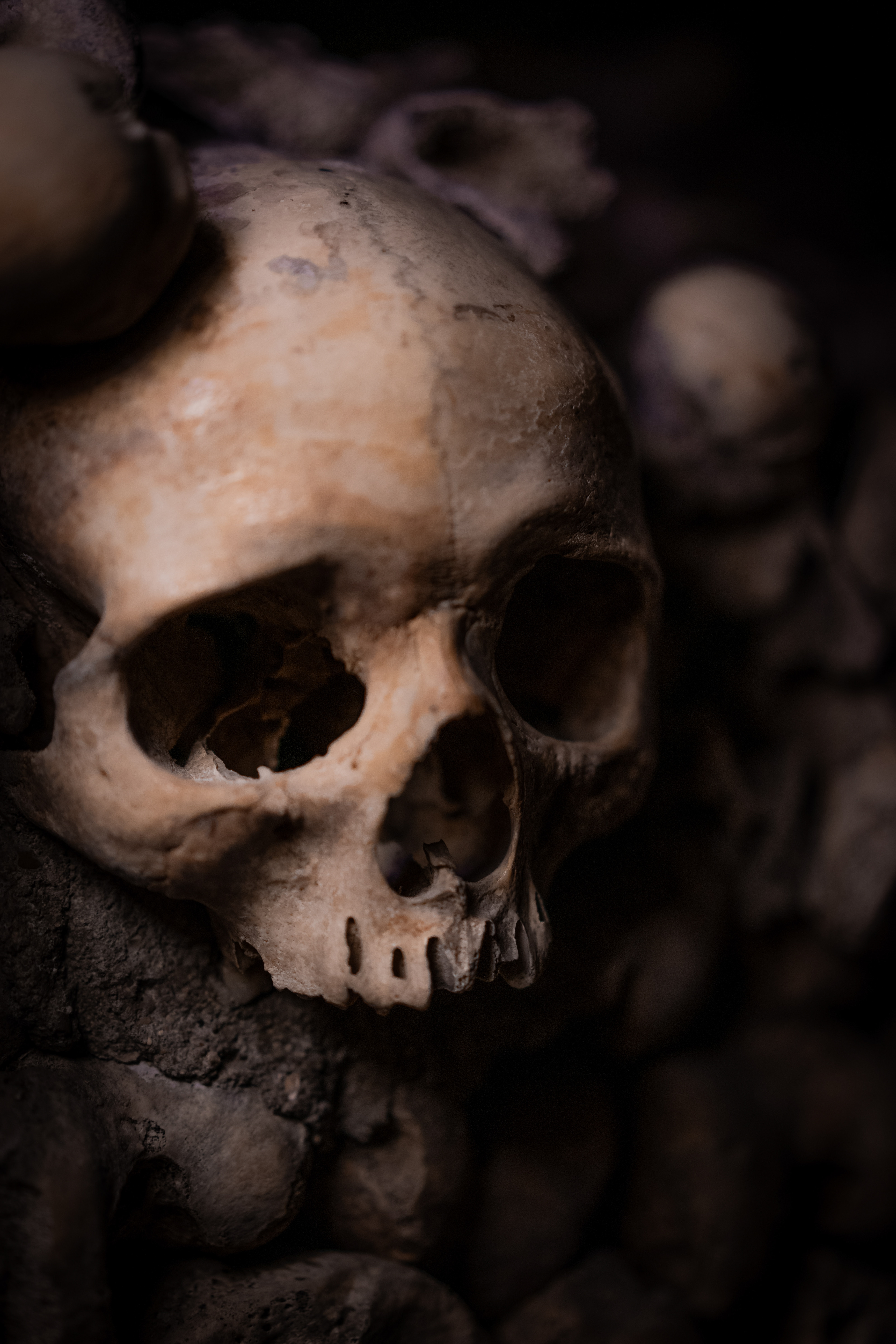
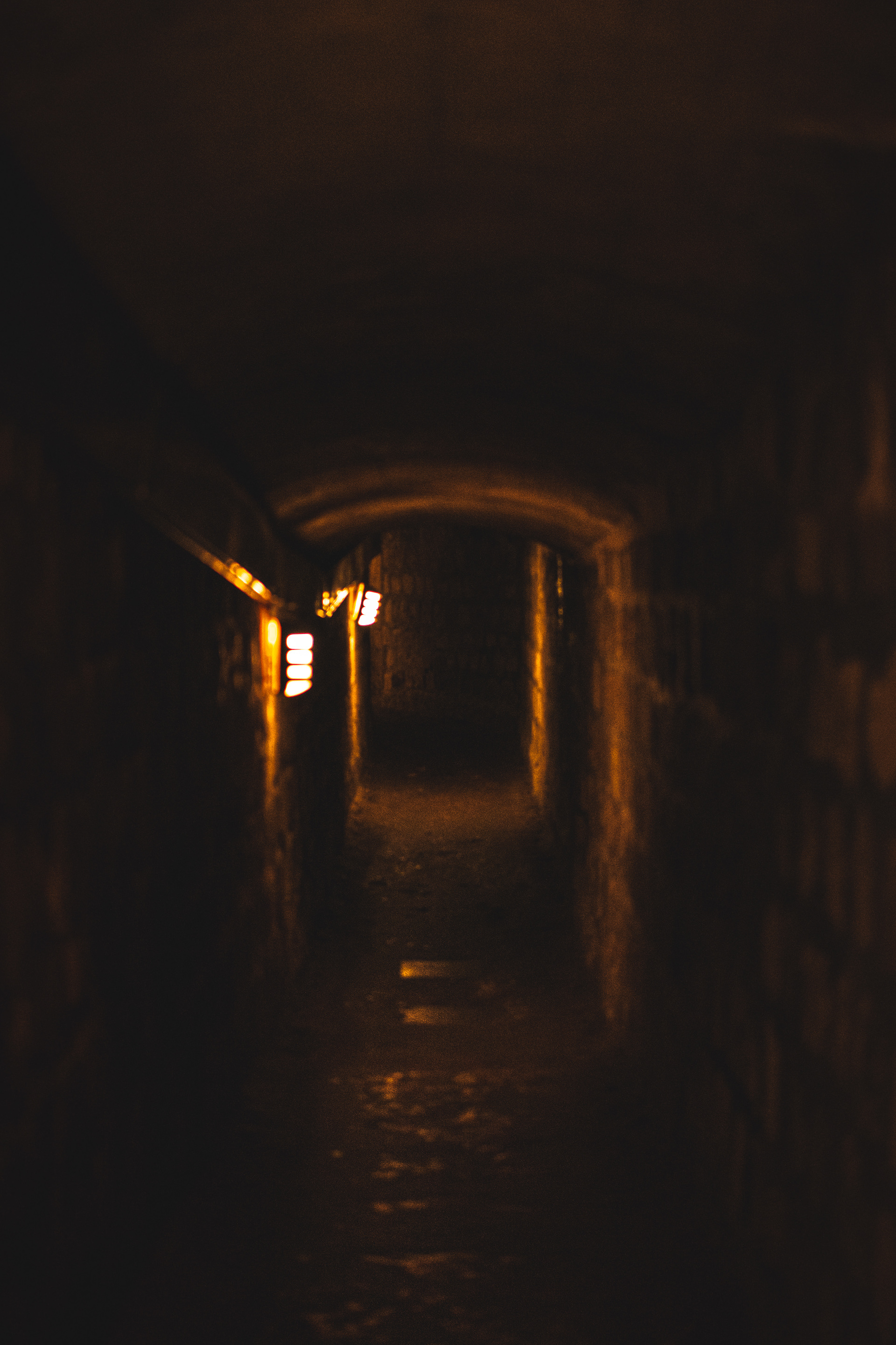










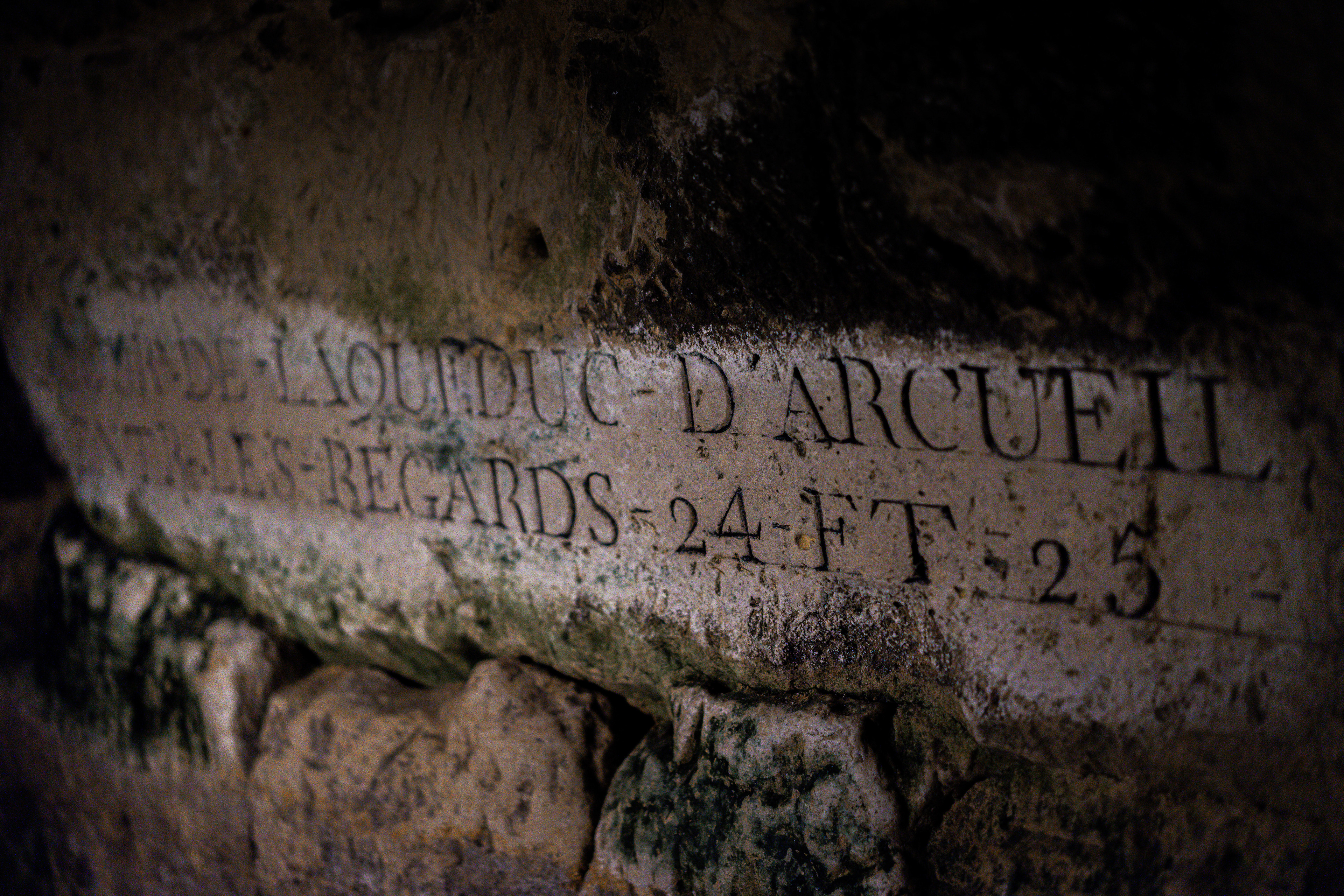

In the late eighteenth century, when major public health problems tied to the city’s cemeteries led to a decision to transfer their contents to an underground site. Paris authorities chose an easily accessible site that was, at the time, located outside the capital: the former Tombe-Issoire quarries under the plain of Montrouge.
The first evacuations were made from 1785 to 1787 and concerned the largest cemetery in Paris, the Saints-Innocents cemetery. The site was consecrated as the “Paris Municipal Ossuary” on April 7, 1786, and, from that time forward, took on the mythical name of “Catacombs”, in reference to the Roman catacombs, which had fascinated the public since their discovery. Starting in 1809, the Catacombs were opened to the public by appointment.





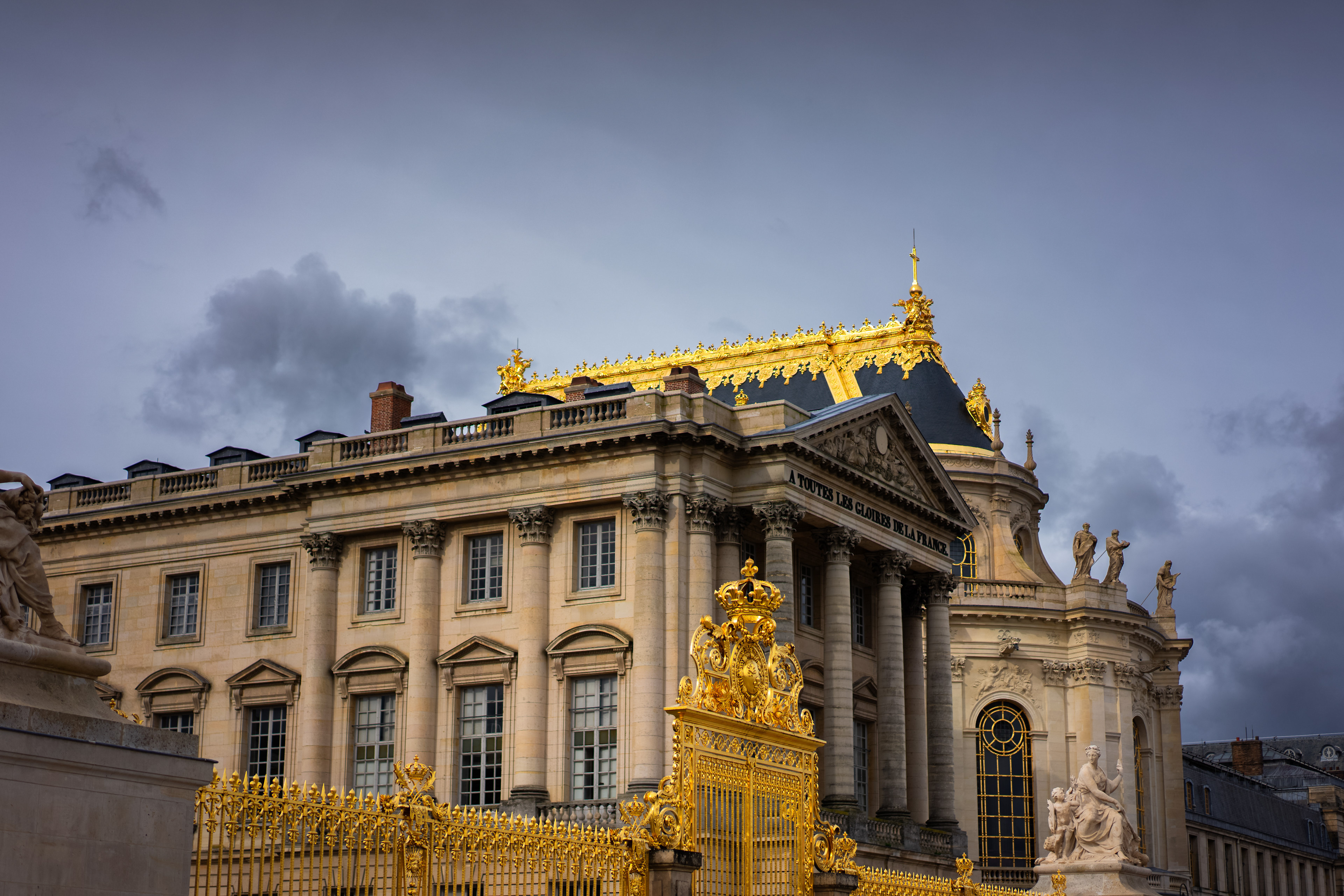
The Palace of Versailles, château de Versailles is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, France.
louis xiii built a simple hunting lodge on the site of the Palace of Versailles in 1623. With his death came Louis XIV who expanded the château into the beginnings of a palace that went through several changes and phases from 1661 to 1715. It was a favourite residence for both kings, and in 1682, Louis XIV moved the seat of his court and government to Versailles, making the palace the de facto capital of France.


















Louis Ernest Ladurée's, a miller, founded a bakery in 1862 on the rue Royale, Paris. During the Paris Commune uprising of 1871, the bakery was burnt down. A pastry shop was built at the same location, and Jules Chéret was entrusted with the interior decoration. The chubby cherubs dressed as pastry cooks, painted by him on the ceiling, form the company's emblem. The interior of the premises were painted in the same celadon colour as the façade.
Ladurée's rise to fame came in 1930 when his little cousin, Pierre Desfontaines, had the original idea of the double-decker, sticking two macaron shells together with a creamy ganache as filling.[5] Queen Catherine de' Medici had brought the macaron to France from Italy in the 16th century, and the recipe for the biscuit had hardly varied over the years, but the amounts of the ingredients used and the appearance of the end product were up to the individual bakers.
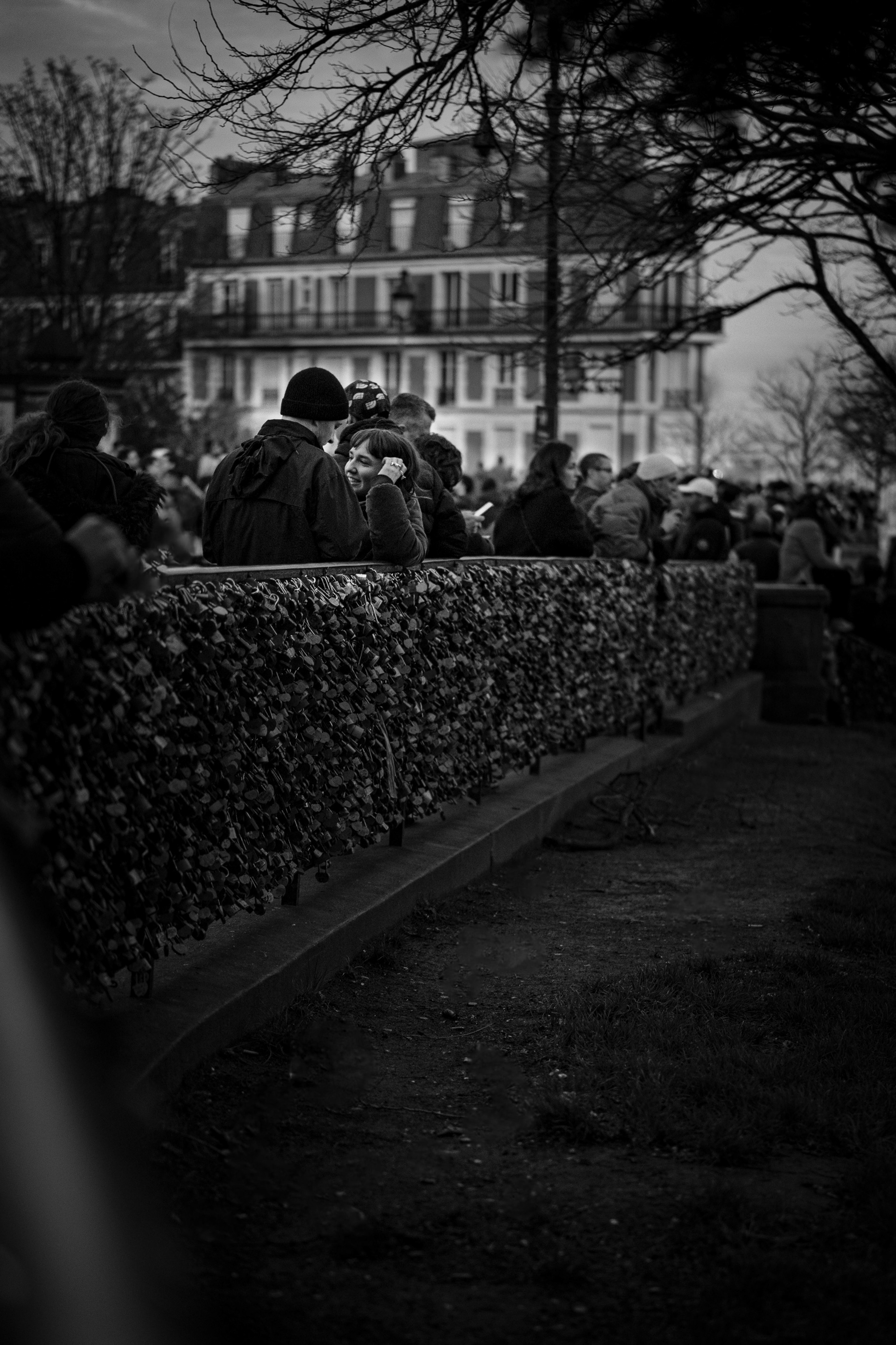
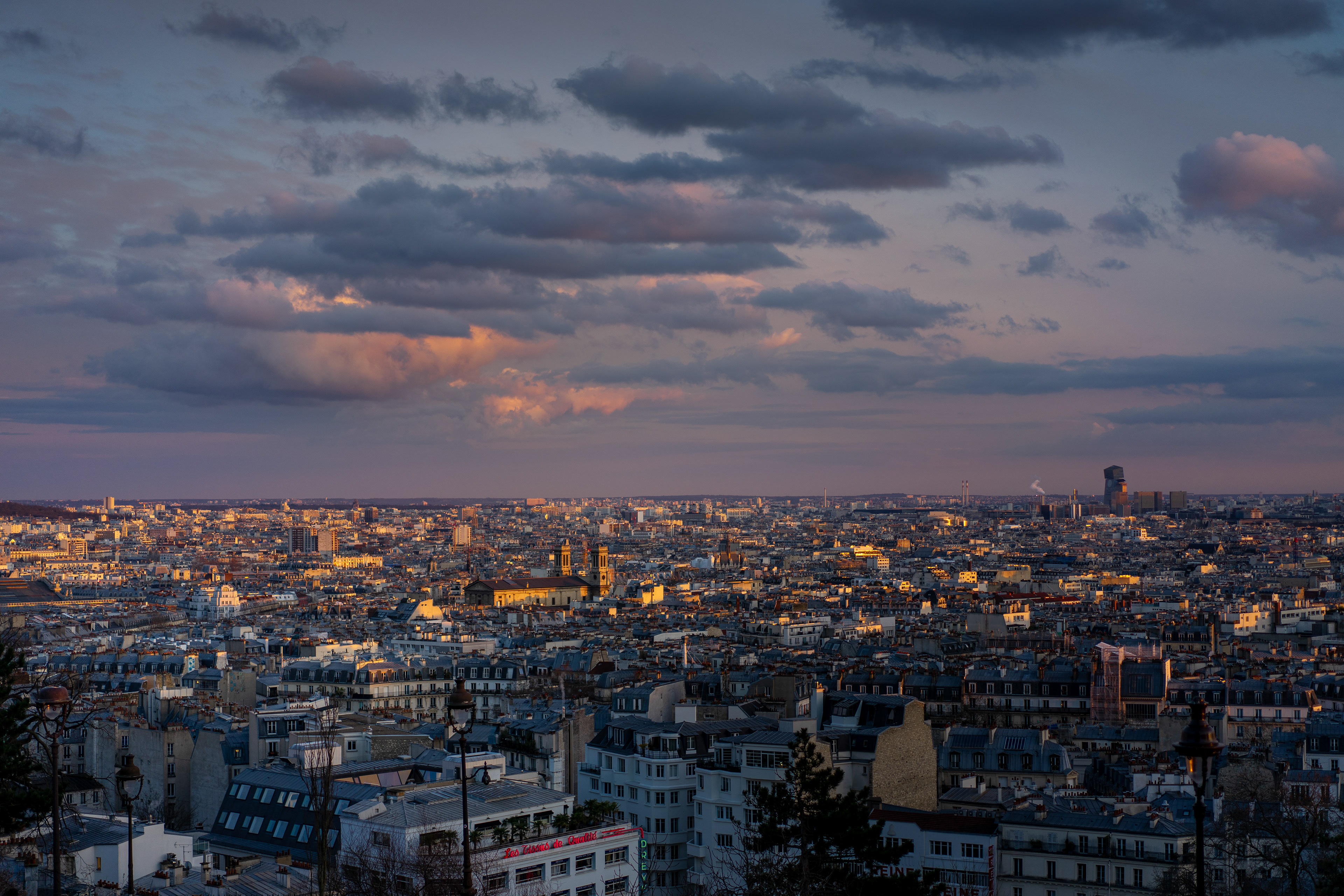
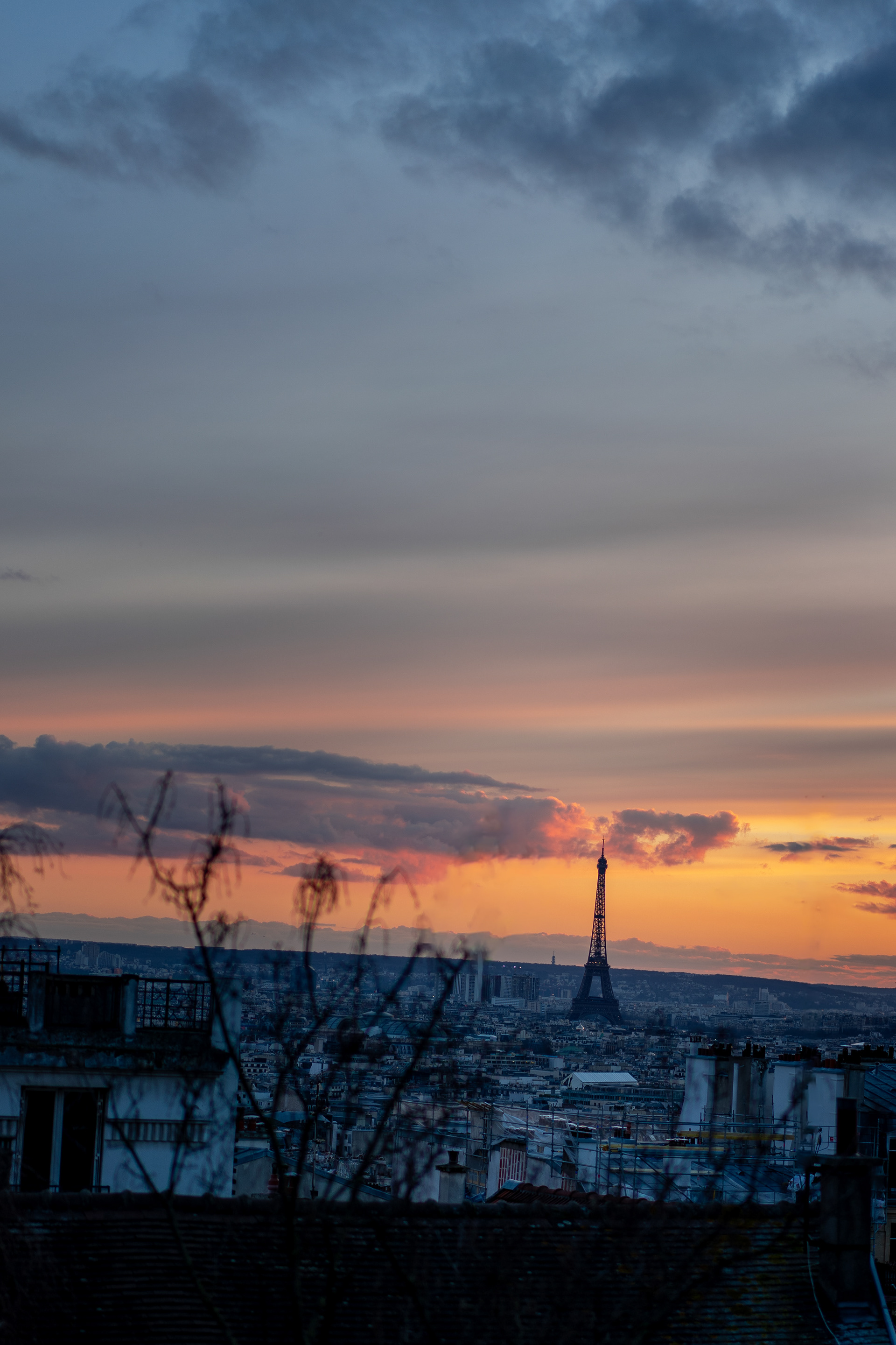










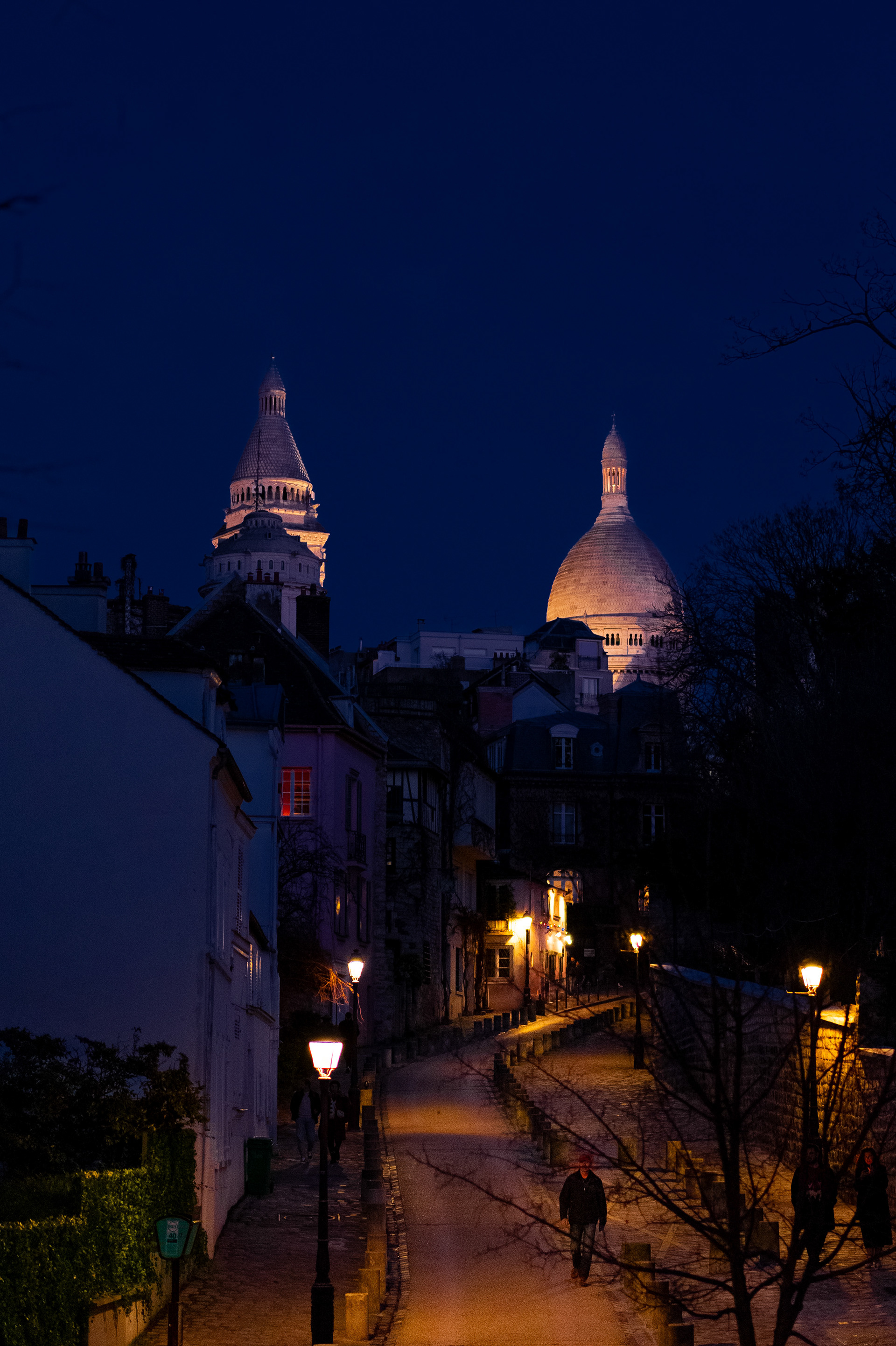
Montmartre is a large hill in Paris's northern 18th arrondissement. It is 130 m (430 ft) high and gives its name to the surrounding district, part of the Right Bank. Montmartre is primarily known for its artistic history, for the white-domed Basilica of the Sacré-Cœur on its summit, and as a nightclub district. Near the end of the 19th century and at the beginning of the 20th, during the Belle Époque, many artists lived, worked, or had studios in or around Montmartre, including Amedeo Modigliani, Claude Monet, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Edgar Degas, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Suzanne Valadon, Piet Mondrian, Pablo Picasso, Camille Pissarro and Vincent van Gogh.
Pierre-Auguste Renoir rented space at 12 rue Cortot in 1876 to paint Bal du moulin de la Galette, showing a dance at Montmartre on a Sunday afternoon. Maurice Utrillo lived at the same address from 1906 to 1914, and Raoul Dufy shared an atelier there from 1901 to 1911. The building is now the Musée de Montmartre.[14] Pablo Picasso, Amedeo Modigliani and other artists lived and worked in a building called Le Bateau-Lavoir during the years 1904–1909, where Picasso painted one of his most important masterpieces, Les Demoiselles d'Avignon.